Plastic recycling is an essential activity for environmental sustainability and the circular economy. However, not all recycling processes are the same. The two most commonly used methods in the industry are chemical plastic recycling and mechanical plastic recycling. In this article, we will explain the differences between these two processes and explore the benefits each offers.
Mechanical plastic recycling is the most common method and involves collecting, sorting, cleaning, and shredding plastic into small particles called flakes. These flakes are melted and molded into pellets that are then sold to manufacture new products. This process is efficient and cost-effective because it does not require the use of additional chemicals. Moreover, mechanical recycling directly contributes to the reduction of plastic pollution by reincorporating leftover materials into the production cycle.
On the other hand, chemical plastic recycling breaks down plastics into their basic chemical components through chemical reactions. This process can convert plastics that are not mechanically recyclable, such as multilayer plastics, into new materials. One of the main advantages of chemical recycling is that it allows for the recycling of a wide range of plastics, including those resins that are difficult to process by mechanical methods.
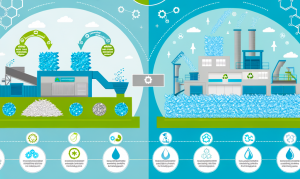
Both methods have significant benefits. Mechanical recycling is generally cheaper and consumes less energy, making it ideal for the most common and easily recyclable plastics. However, chemical recycling has the advantage of expanding the spectrum of recyclable plastics and can be fundamental in the transition to a completely circular economy, where all types of plastics can be reused.
In summary, both mechanical and chemical plastic recycling have important roles to play in the sustainable management of plastic waste. The choice between one method or another depends on the type of plastic and the specific objectives to be achieved.

